Big Data and Cloud in Vertical Farming-Based IoT Solutions
Vertical farming-based IoT solutions are one of the key emerging trends in the agriculture industry today.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeVertical farming-based IoT solutions are one of the key emerging trends in the agriculture industry today. These solutions are not only providing accurate information on plant growth statistics but also making operations more sustainable. With these solutions, farmers can track energy usage and soil composition, verify air quality, temperature and moisture levels, etc. and perform operations in a more efficient manner.
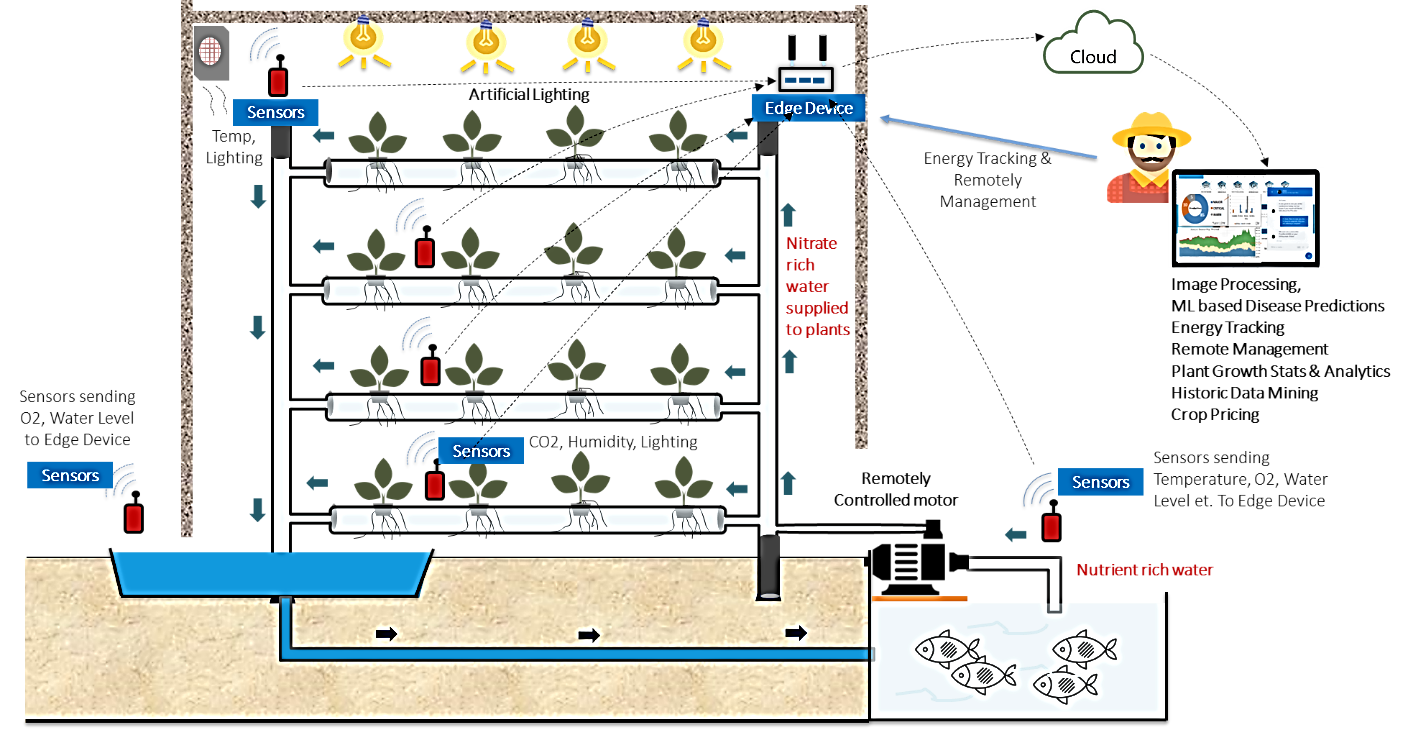
In addition to processing data at rest, the real-time processing of sensor data i.e., the ability to process data collected by various sensors as it arrives, would form the major building blocks of these kinds of solutions. However, traditional data processing systems fall behind in handling real-time data, unstructured data, and scaling on demand. This is the reason why the usage of big data on the cloud in IoT-based solutions is on the rise, as it would require querying continuous data streams and detecting conditions quickly within a small interval from the time of receiving it. While big data supports data storage and structured as well as unstructured data processing, whereas cloud services are used for cost-effective scalable infrastructure.
Two prominent big data processing techniques useful for these kinds of scenarios are:
- Lambda Architecture
- Kappa Architecture
I have already discussed Lambda architecture in detail here. Though lambda has a fault-tolerant and scalable architecture along with the batch layer, which manages historical data in a distributed fashion, the major drawbacks of this model are:
- Batch and streaming layers each require a different codebase to be maintained and kept in sync.
- It can result in coding overhead due to the involvement of comprehensive processing.
- Batch, speed, and serving layers, all need to be processed (at least) twice.
- A data modeled with Lambda architecture is difficult to migrate or reorganize.
The Kappa architecture is an event-driven software architecture model that can handle real-time data at scale for transactional and analytical systems. The major advantage of this model is that both real-time, as well as batch processing can be performed with a single technology stack. The heart of the infrastructure is the streaming architecture. First, the event streaming platform log stores incoming data. Later, the stream processing engine processes or ingests the real-time data continuously into the knowledge store or analytics database. An IoT-based reference model using cloud data processing stream analytics services is shown below: 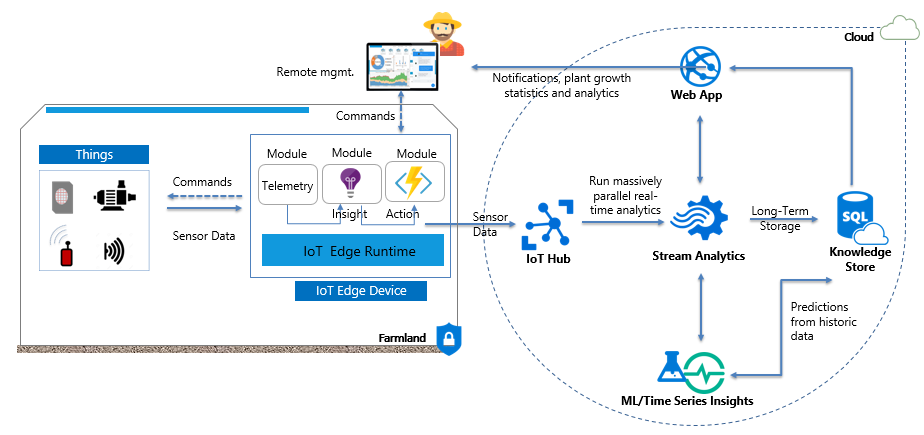
- IoT Clients or Edge Devices that can have multiple sensors installed and can send records with measurements reported by all sensors. The devices can:
- Extend cloud intelligence to edge devices.
- Run artificial intelligence at the edge.
- Perform edge analytics.
- Deploy IoT solutions from the cloud to the edge.
- IoT Hubs: Services that enable reliable and secure bi-directional communication between IoT devices and Cloud services. IoT hubs can:
- Manage devices centrally from the cloud.
- Operate with offline and intermittent connectivity.
- Enable real-time decisions.
- Connect new and legacy devices.
- Reduce bandwidth costs.
- Stream Processors that consume that data, integrate it with business processes and place the data into storage.
- ML/Time Series Insights: Which allows predictive algorithms to be executed over historical telemetry data, enabling scenarios such as predictive maintenance.
- Knowledge Store for storing historical data and earlier predictions. This store can also be enriched with real-time market prices, pesticides, and other agriculture product-related information.
- Web App: A user interface to display plant and crop statistics and display of other telemetry data, which helps farmers with quick decision-making.
With the cloud-based data processing techniques, intelligence can be built into these models by collecting data from IoT things equipped with sensors that continuously act on the data and transmit it to data processing locations. Remotely track energy usage, soil composition, or water levels, and remote actions like ML-based Disease Predictions, Artificial Lighting, and Control, etc., can be performed.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments