Blockchain: An Introduction
Blockchain is one of the more promising technologies out there when it comes to cybersecurity. Read on to find you why, and what issues blockchain is facing.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBlockchain is so hot in the market nowadays and its adoption has grown extensively in various industries including retail, healthcare, IoT, and finance/banking. Blockchain is commonly associated with the technology behind Bitcoin, but it is much more than a way to document crypto-currencies, and it has the potential to fit into any form of digital assets and data that may come out. The processes which involve manual operations where a trusted third party is facilitating a transaction can be automated using Blockchain and two parties can enter into a transaction without a middleman. This could enable organizations to carry out complex processes cheaper and easier.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed database which maintains a continuously growing list of records (here list of records could be understood as a LinkedList), known as 'Blocks'; (a Block is the same as a Node in LinkedList). Each block has two parts (just as a Node in a LinkedList has two parts - the data and the address of the next Node); a timestamp with transaction data, and a link (a hash pointer) to the previous block.
Blockchains are not meant for modification and deletion of data. Hence, once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be modified/erased without the modification of all subsequent blocks and the collusion of the network. It means they can be sequentially updated whenever a modification is needed.
A blockchain is based on the Distributed Ledger Technology (a shared ledger across the network), which helps transactions to have public witnesses and hence minimize cyber crime and fraud. This serves as an open, distributed ledger to record transactions between two parties in a verifiable and lasting way.
A blockchain is connected by a P2P network ( a network of nodes/computers where each node is an Admin), which enables a protocol for validating new blocks (below diagram) and relaying transactions. A new node gets a copy of the blockchain after joining the network. The distributed ledger has the capability to be programmed, hence the transactions can be triggered automatically.
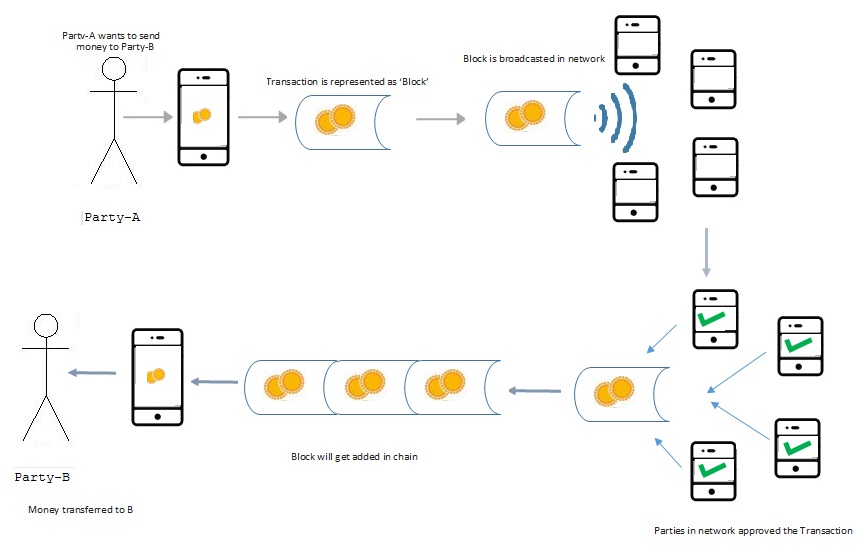
Let us look at an example, where two parties are involved in a money exchange transaction.
Suppose Party-A wants to send money to Party-B; so the transaction would be represented online as a 'Block.' Now the Block would be broadcast to every party in the network. All parties in the network will approve the transaction if valid (a block is valid only if it obeys all the protocol rules). If it is invalid, it will not be relayed. The Block then can be added to the chain, which provides a lasting and transparent record of transactions. Now the money moves to Party-B.
There are three aspects of any technology - technical, business, and legal - and the same applies to a Blockchain as well. As a technologist, you can think of Blockchain as backend database which has a distributed ledger. As a business professional, you can think of it as an exchange network, which transfers data between peers. As a legal and compliance specialist, this can be thought of as a way to validate transactions.
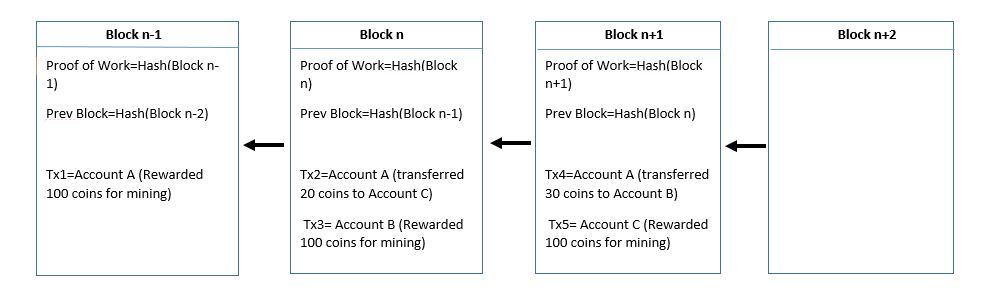
Let us look at the structure of a 'Block.'
Each block is chained to the other blocks like a linked list. Here each block is using the hash value of the previous block to form a chain. As you can see in the below diagram, the transactions are being recorded in the blocks.
Blockchain technology is being explored and evaluated by most financial institutions and banks in several ways. Possible applications that are in POC (Proof of Concept) stage or have been implemented are P2P money transfer, cross border payments, digital currency exchange, trade finance, smart contracts, and risk management.
The major challenges are regulatory compliance, policies, and legal frameworks to support the technology's adaptation.
Hope this helped you an understand this cutting-edge technology a litte better.
Happy learning!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments