Decoding Exponential Backoff: A Blueprint for Robust Communication
Exponential Backoff is a network algorithm that prevents overload during outages and can be useful for distributed systems.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeExponential backoff is a network algorithm that gradually increases the time between successive retries when a request to a server fails. This mechanism is commonly used in distributed systems and networking protocols to handle situations where a server is temporarily unavailable or overloaded. The goal is to prevent overwhelming the server with repeated requests and to allow the system to recover from transient failures.
Need for Exponential Backoff
- Avoiding Overloading Servers: In cases of server outages or high load, repeated and immediate retries can contribute to server overload. Exponential backoff helps distribute retries over time, reducing the risk of further overwhelming the server.
- Handling Transient Failures: Transient failures, which are temporary and typically resolve themselves, can be mitigated by giving the system some time to recover before attempting another connection.
Implementation Details
1. Initial Timeout: Start with an initial timeout value for the first retry attempt.
2. Exponential Increase: For each subsequent retry, multiply the timeout value by a factor (commonly 2). This exponentially increases the time between retries.
3. Randomization: Introduce a randomization element to avoid synchronization issues and reduce the likelihood of simultaneous retries from multiple clients.
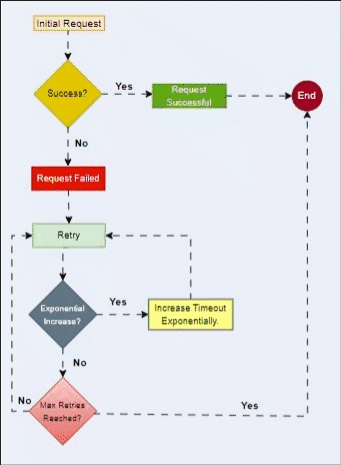
Here's a simple example of implementing exponential backoff in Java. In this example, we'll use a method that simulates making a network request and retries with exponential backoff if there's a failure.
import java.util.Random;
public class ExponentialBackoffExample {
private static final int MAX_RETRIES = 5;
private static final int BASE_TIMEOUT = 1000; // 1 second
private static final int BACKOFF_FACTOR = 2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
performNetworkRequest();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Network request failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private static void performNetworkRequest() throws InterruptedException {
int retries = 0;
Random random = new Random();
while (retries < MAX_RETRIES) {
try {
// Simulate a network request (replace with your actual code)
System.out.println("Making network request...");
if (random.nextDouble() < 0.8) { // Simulate an 80% success rate
System.out.println("Network request successful!");
return;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Network error");
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
System.out.println("Network request failed: " + e.getMessage());
retries++;
if (retries < MAX_RETRIES) {
// Calculate the backoff time with exponential increase
int backoffTime = (int) (BASE_TIMEOUT * Math.pow(BACKOFF_FACTOR, retries));
System.out.println("Retrying in " + backoffTime + " milliseconds...");
Thread.sleep(backoffTime);
} else {
System.out.println("Max retries reached. Giving up.");
throw e; // If you want to propagate the exception after all retries
}
}
}
}
}In this example, the performNetworkRequest method simulates a network request that may fail. If a failure occurs, it retries with exponential backoff up to a maximum number of retries (MAX_RETRIES). The backoff time is calculated using the BASE_TIMEOUT and BACKOFF_FACTOR. The Thread.sleep method is used to pause the execution for the calculated backoff time before the next retry. This is a basic example, and you may need to adapt it based on your specific use case and requirements.
Advantages of Exponential Backoff
- Server Load Management: Prevents overwhelming the server with repeated connection attempts during high load or outages.
- System Resilience: Helps systems recover from transient failures by allowing time for the issues to be resolved.
- Reduced Network Congestion: Distributes retry attempts over time, reducing the likelihood of network congestion.
Limitations of Exponential Backoff
- Increased Latency: The exponential increase in timeout values can lead to increased latency for certain types of failures.
- Not Suitable for All Scenarios: In some scenarios, immediate retries might be more appropriate, especially for non-transient errors.
In summary, exponential backoff stands as a valuable strategy in mitigating the impact of temporary disruptions, contributing to the overall robustness and reliability of distributed systems and network communications.
Published at DZone with permission of Roopa Kushtagi. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments