Decoding the Differences: Continuous Integration, Delivery and Deployment
Join us on this informative journey as we unravel the distinctions between CI, CD, and CD. We’ll dive deep into these concepts in detail in this blog!
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the fast-paced world of software development, concepts like Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery (CD), and Continuous Deployment (CD) play a vital role in streamlining the development and delivery process. These practices have revolutionized the way software is developed, tested, and deployed, enabling organizations to deliver high-quality applications more efficiently.
However, with their similar-sounding names, it's crucial to understand the nuances and differences between Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery, and Continuous Deployment. Here, in this blog, we will dive deep into each of these DevOps concepts, explore their unique characteristics, and learn how they contribute to the software development process.
So, join us on this informative journey as we unravel the distinctions between CI, CD, and CD. Explore these concepts and gain insights into how they can empower your development teams to build, test, and deliver software more efficiently, ensuring a seamless and reliable application delivery process. Let's explore Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery, and Continuous Deployment together!
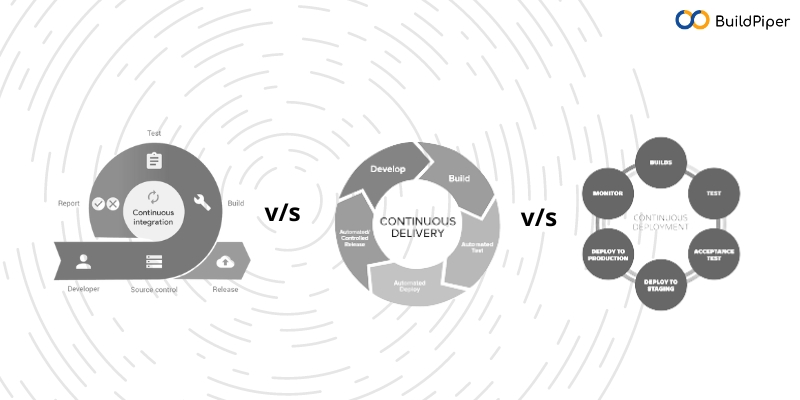
What Is Continuous Integration?
Continuous Integration (CI) is a software development practice that involves frequently integrating code changes from multiple developers into a shared repository. The main objective of CI is to identify integration issues and bugs early in the development process, ensuring that the software remains in a consistent and working state.
In this DevOps practice, developers regularly commit their code changes to a central version control system, triggering an automated build process. This process compiles the code, runs automated tests, and performs various checks to validate the changes. If any issues arise during the build or testing phase, developers are notified immediately, enabling them to address the problems promptly.
By embracing CI, development teams can reduce the risks associated with integrating new code and detect issues early. Ultimately, this leads to faster feedback loops and quicker bug resolution. It promotes collaboration, improves code quality, and helps deliver reliable software at a faster pace.
What Is Continuous Delivery?
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a software development practice that focuses on automating the release process to enable frequent and reliable software deployments. It aims to ensure that software can be released at any time, allowing organizations to deliver new features, enhancements, and bug fixes to end-users rapidly and consistently.
In continuous delivery, the code undergoes automated tests and quality checks as part of the software delivery pipeline. These tests verify the integrity and functionality of the application, including unit tests, integration tests, performance tests, and security scans. If the code changes pass all the required tests and meet the predefined quality criteria, they are considered ready for deployment.
The key principle of this DevOps practice is to keep the software deployable at all times. While the decision to release the software to production is still a manual process, the automation of the delivery pipeline ensures that the software is in a releasable state at any given moment.
Continuous delivery promotes collaboration, transparency, and efficiency in the software development process. It minimizes the risk of human error, accelerates time-to-market, and helps teams in seamless DevOps implementation. This process enables organizations to respond quickly to market demands and customer feedback. It also sets the foundation for continuous deployment, where changes are automatically deployed to production once they pass the necessary tests.
What Is Continuous Deployment?
Continuous Deployment (CD) is a software development approach where changes to an application's codebase are automatically and frequently deployed to production environments. It is an extension of continuous integration (CI) and aims to streamline the software delivery process by minimizing manual intervention and reducing the time between development and deployment.
In continuous deployment, once code changes pass through the CI pipeline and automated tests successfully, the updated application is automatically deployed to production without human intervention. This process eliminates the need for manual release approvals and accelerates the delivery of new features, enhancements, and bug fixes to end-users.
Continuous deployment relies on automated software testing, quality assurance practices, and a highly automated deployment pipeline. It requires a high level of confidence in the stability and reliability of the application. This is because any code changes that pass the necessary tests are instantly deployed to the live environment.
By embracing continuous deployment, organizations can achieve faster time-to-market, increased agility, and improved responsiveness to user feedback. It also encourages a culture of automation and continuous improvement in software development processes.
Differences Between Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery, and Continuous Deployment
Here are the key differences between Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery (CD) and Continuous Deployment (CD):
Continuous Integration (CI)
- Focus: CI focuses on integrating code changes from multiple developers into a shared repository frequently.
- Objective: The main goal of CI is to catch integration issues and bugs early in the development process, ensuring a consistent and working codebase.
- Process: Developers regularly commit their code changes to a central version control system, triggering an automated build process. Automated tests are executed during the build to verify code functionality and integrity.
- Manual Intervention: CI does not involve automatic deployment to production. The decision to release the software to production is typically a manual process.
Benefits: CI promotes collaboration among developers, improves code quality, and enables faster feedback loops for quicker bug resolution.
Continuous Delivery (CD)
- Focus: CD extends CI and focuses on automating the software delivery process.
- Objective: CD aims to ensure that software can be reliably and consistently delivered to various environments, including staging and production.
- Process: CD includes automating various stages of the software delivery pipeline, such as automated software testing, packaging, and deployment. It maintains the software in a release-ready state, ready for deployment at any time.
- Manual Intervention: While CD keeps the software ready for deployment, the decision to release it to production typically involves a manual step for approval.
- Benefits: CD enables fast and reliable releases, reduces time-to-market, and allows teams to respond quickly to market demands.
Continuous Deployment (CD)
- Focus: CD takes automation further by automatically deploying code changes to production environments.
- Objective: The primary objective of CD is to achieve rapid and frequent releases to end-users.
- Process: CD automates the deployment process, ensuring that code changes meeting the necessary tests and release criteria are automatically deployed to production without human intervention.
- Manual Intervention: CD eliminates the need for manual release approvals or interventions for code deployment.
- Benefits: CD enables organizations to achieve a high degree of automation, delivering software quickly and reliably to end-users.
CI focuses on integrating code changes, and CD (Continuous Delivery) automates the software delivery process. Ultimately, CD (Continuous Deployment) takes automation further by automatically deploying changes to production. While CI ensures integration and code quality, CD (Continuous Delivery) focuses on reliable and consistent software delivery. CD (Continuous Deployment) automates the deployment process for rapid and frequent releases.
Together, CI/CD practices foster a culture of automation, collaboration, and rapid delivery, aligning well with the principles of DevOps. By adopting CI/CD, organizations can achieve faster time-to-market, higher software quality, and increased agility in responding to user feedback and market demands.
Published at DZone with permission of Ruchita Varma. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments