Exploring the Horizon of Microservices With KubeMQ's New Control Center
Dealing with the complexities of microservice communication can be a burden. Here, learn how developers can be more efficient using microservice architectures.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe software development landscape is rapidly evolving. New tools, technologies, and trends are always bubbling to the top of our workflows and conversations. One of those paradigm shifts that has become more pronounced in recent years is the adoption of microservices architecture by countless organizations.
Managing microservices communication has been a sticky challenge for many developers. As a microservices developer, I want to focus my efforts on the core business problems and functionality that my microservices need to achieve. I’d prefer to offload the inter-service communication concerns—just like I do with authentication or API security.
So, that brings me to the KubeMQ Control Center (KCC). It’s a service for managing microservices communication that’s quick to set up and designed with an easy-to-use UI. In this article, I wanted to unpack some of the functionality I explored as I tested it in a real-world scenario.
Setting the Scene
Microservices communication presents a complex challenge, akin to orchestrating a symphony with numerous distinct instruments. It demands precision and a deep understanding of the underlying architecture. Fortunately, KCC—with its no-code setup and Kubernetes-native integration—aims to abstract away this complexity. Let's explore how it simplifies microservices messaging.
Initial Setup and Deployment
Deploy KubeMQ Using Docker
The journey with KCC starts with a Docker-based deployment. This process is straightforward:
$ docker run -d \
-p 8080:8080 \
-p 50000:50000 \
-p 9090:9090 \
-e KUBEMQ_TOKEN=(add token here) kubemq/kubemqThis command sets up KubeMQ, aligning the necessary ports and establishing secure access.
Send a "Hello World" Message
After deployment, you can access the KubeMQ dashboard in your browser at http://localhost:8080/. Here, you have a clean, intuitive UI to help you manage your microservices.
We can send a “Hello World” message to test the waters. In the Dashboard, click Send Message and select Queues.

We set a channel name (q1) and enter "hello world!" in the body. Then, we click Send.

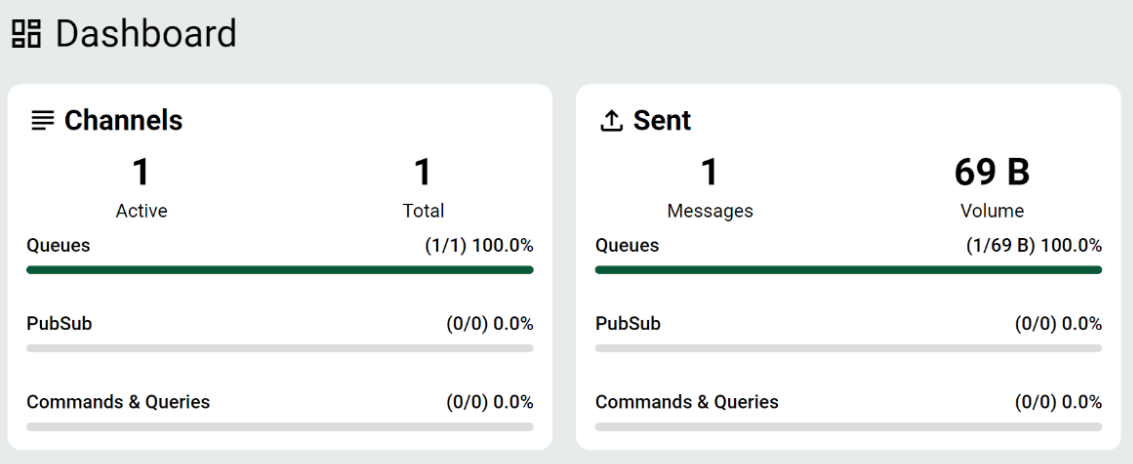
Just like that, we successfully created our first message! And it’s only been one minute since we deployed KubeMQ and started using KCC.
Pulling a Message
Retrieving messages is a critical aspect of any messaging platform. From the Dashboard, select your channel to open the Queues page.
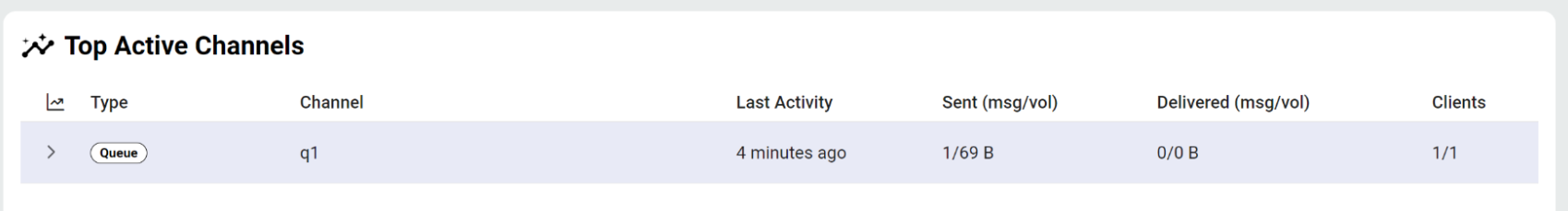
Under the Pull tab, click Pull to retrieve the message that you just sent. The process is pretty smooth and efficient.
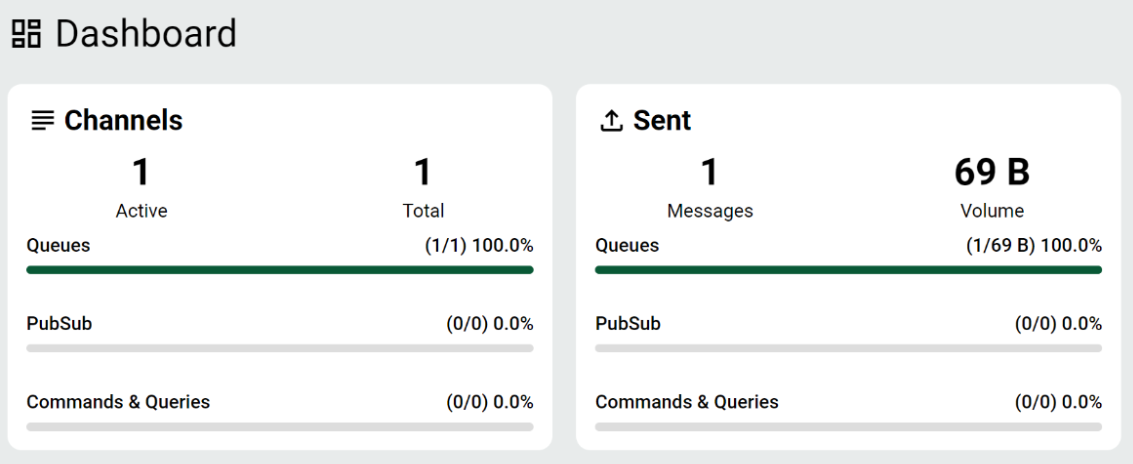
We can review the message details for insights into its delivery and content.

Send “Hello World” With Code
Moving beyond the UI, we can send a “Hello world” message programmatically too. For example, here’s how you would send a message using C#.
KCC integrates with most of the popular programming languages, which is essential for diverse development environments. Here are the supported languages and links to code samples and SDKs:
Deploying KubeMQ in Kubernetes
Transitioning to Kubernetes with KCC is pretty seamless, too. KubeMQ is shooting to design with scalability and the developer in mind. Here’s a quick guide to getting started.
Download KCC
Download KCC from KubeMQ’s account area. They offer a 30-day free trial so you can do a comprehensive evaluation.
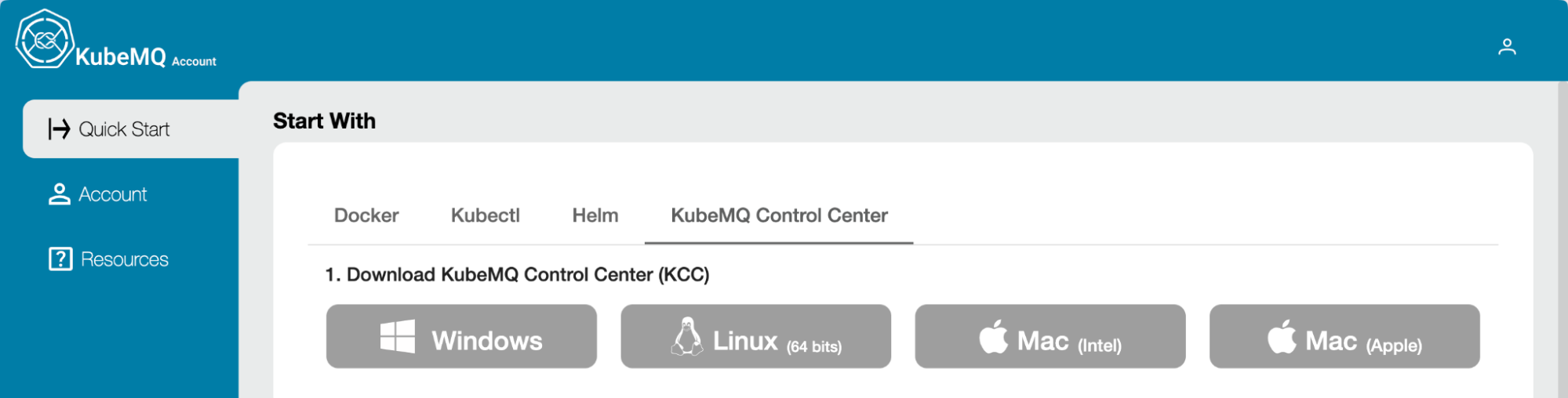
Unpack the Zip File
$ unzip kcc_mac_apple.zip -d /kubemq/kccLaunch the Application
$ ./kccThe above step integrates you into the KubeMQ ecosystem, which is optimized for Kubernetes.
Add a KubeMQ Cluster
Adding a KubeMQ cluster is crucial for scaling and managing your microservices architecture effectively.

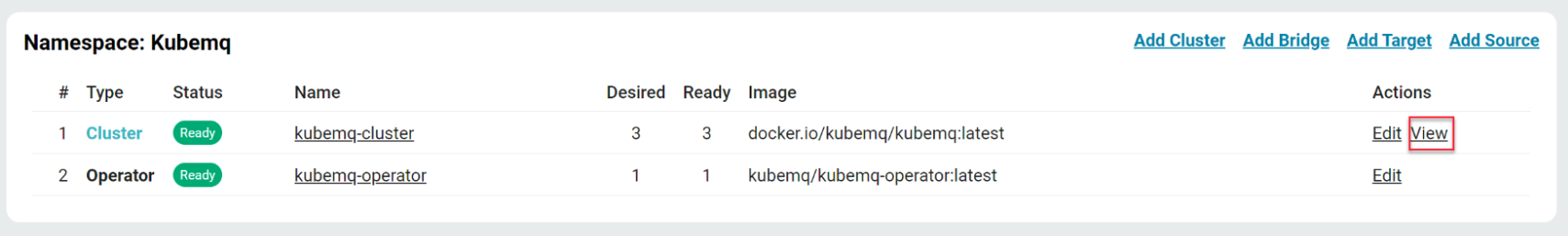
Monitor Cluster Status
The dashboard provides an overview of your KubeMQ components, essential for real-time system monitoring.
Explore Bridges, Targets, and Sources
KCC has advanced features like Bridges, Targets, and Sources, which serve as different types of connectors between KubeMQ clusters, external messaging systems, and external cloud services. These tools will come in handy when you have complex data flows and system integrations, as many microservices architectures do.
Conclusion
That wraps up our journey through KubeMQ's Control Center. Dealing with the complexities of microservice communication can be a burden, taking the developer away from core business development. Developers can offload that burden to KCC. With its intuitive UI and suite of features, KCC helps developers be more efficient as they build their applications on microservice architectures.
Of course, we’ve only scratched the surface here. Unlocking the true potential of any tool requires deeper exploration and continued use. For that, you can check out KubeMQ’s docs site. Or you can build on what we’ve shown above, continuing to play around on your own. With the right tools in your toolbox, you’ll quickly be up and running with a fleet of smoothly communicating microservices!
Have a really great day!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments