NIST AI Risk Management Framework: Developer’s Handbook
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework offers a comprehensive approach to addressing the complex challenges associated with managing risks in AI technologies.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe NIST AI RMF (National Institute of Standards and Technology Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework) provides a structured framework for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with artificial intelligence technologies, addressing complex challenges such as algorithmic bias, data privacy, and ethical considerations, thus helping organizations ensure the security, reliability, and ethical use of AI systems.
How Do AI Risks Differ From Traditional Software Risks?
AI risks differ from traditional software risks in several key ways:
- Complexity: AI systems often involve complex algorithms, machine learning models, and large datasets, which can introduce new and unpredictable risks.
- Algorithmic bias: AI systems can exhibit bias or discrimination based on factors such as the training data used to develop the models. This can result in unintended outcomes and consequences, which may not be part of traditional software systems.
- Opacity and lack of interpretability: AI algorithms, particularly deep learning models, can be opaque and difficult to interpret. This can make it challenging to understand how AI systems make decisions or predictions, leading to risks related to accountability, transparency, and trust.
- Data quality and bias: AI systems rely heavily on data, and issues such as data quality, incompleteness, and bias can significantly impact their performance and reliability. Traditional software may also rely on data, but the implications of data quality issues may be more noticeable in AI systems, affecting the accuracy, and effectiveness of AI-driven decisions.
- Adversarial attacks: AI systems may be vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where malicious actors manipulate inputs to deceive or manipulate the system's behavior. Adversarial attacks exploit vulnerabilities in AI algorithms and can lead to security breaches, posing distinct risks compared to traditional software security threats.
- Ethical and societal implications: AI technologies raise ethical and societal concerns that may not be as prevalent in traditional software systems. These concerns include issues such as privacy violations, job displacement, loss of autonomy, and reinforcement of biases.
- Regulatory and compliance challenges: AI technologies are subject to a rapidly evolving regulatory landscape, with new laws and regulations emerging to address AI-specific risks and challenges. Traditional software may be subject to similar regulations, but AI technologies often raise novel compliance issues related to fairness, accountability, transparency, and bias mitigation.
- Cost: The expense associated with managing an AI system exceeds that of regular software, as it often requires ongoing tuning to align with the latest models, training, and self-updating processes.
Effectively managing AI risks requires specialized knowledge, tools, and frameworks tailored to the unique characteristics of AI technologies and their potential impact on individuals, organizations, and society as a whole.
Key Considerations of the AI RMF
The AI RMF refers to an AI system as an engineered or machine-based system that can, for a given set of objectives, generate outputs such as predictions, recommendations, or decisions influencing real or virtual environments. The AI RMF helps organizations effectively identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks associated with AI technologies throughout the lifecycle. It addresses various challenges, like data quality issues, model bias, adversarial attacks, algorithmic transparency, and ethical considerations. Key considerations include:
- Risk identification
- Risk assessment and prioritization
- Control selection and tailoring
- Implementation and integration
- Monitoring and evaluation
- Ethical and social implications
- Interdisciplinary collaboration
Key Functions of the Framework
Following are the essential functions within the NIST AI RMF that help organizations effectively identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks associated with AI technologies.
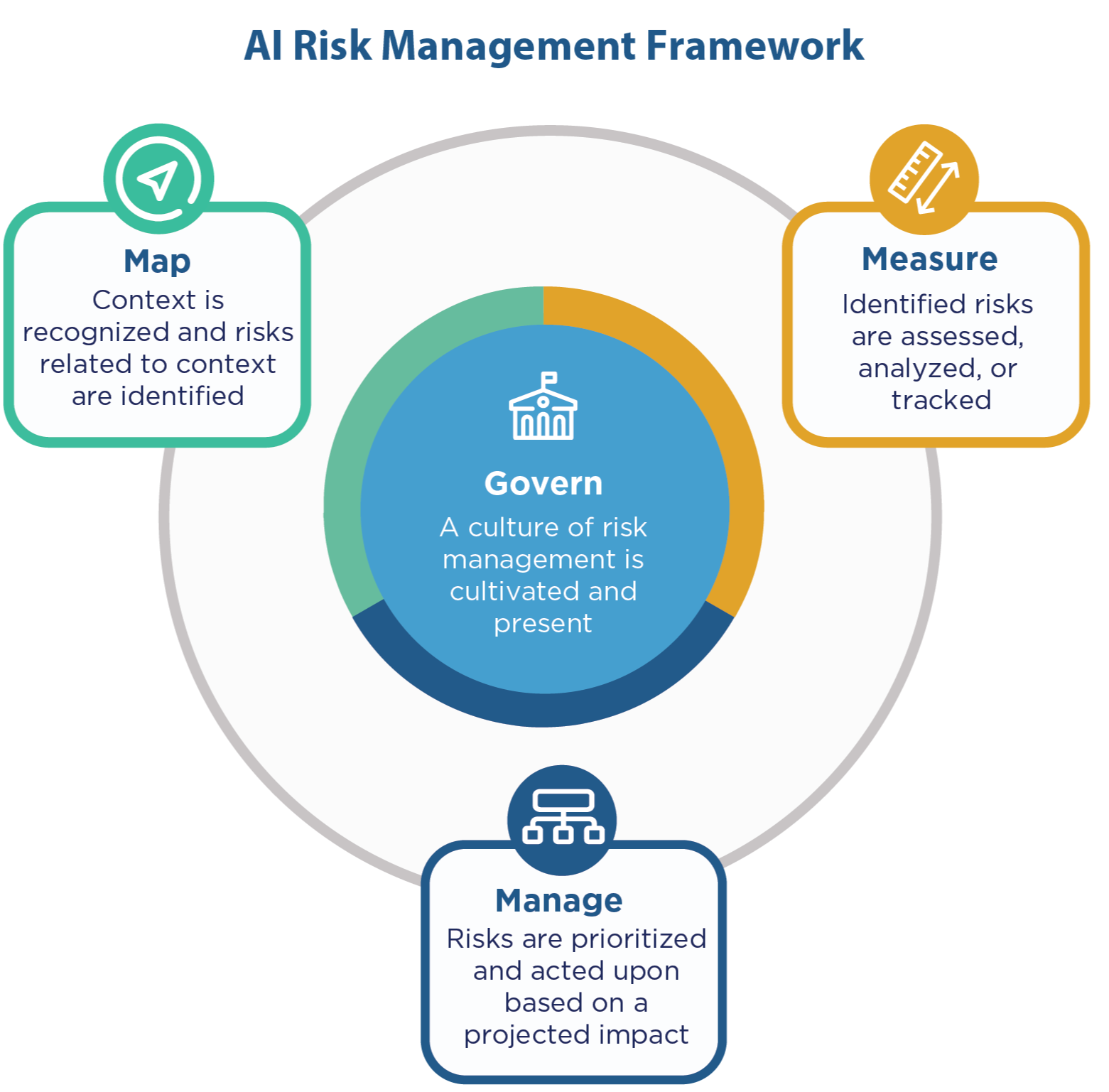
Image courtesy of NIST AI RMF Playbook
Govern
Governance in the NIST AI RMF refers to the establishment of policies, processes, structures, and mechanisms to ensure effective oversight, accountability, and decision-making related to AI risk management. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, setting risk tolerance levels, establishing policies and procedures, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and organizational objectives. Governance ensures that AI risk management activities are aligned with organizational priorities, stakeholder expectations, and ethical standards.
Map
Mapping in the NIST AI RMF involves identifying and categorizing AI-related risks, threats, vulnerabilities, and controls within the context of the organization's AI ecosystem. This includes mapping AI system components, interfaces, data flows, dependencies, and associated risks to understand the broader risk landscape. Mapping helps organizations visualize and prioritize AI-related risks, enabling them to develop targeted risk management strategies and allocate resources effectively. It may also involve mapping AI risks to established frameworks, standards, or regulations to ensure comprehensive coverage and compliance.
Measurement
Measurement in the NIST AI RMF involves assessing and quantifying AI-related risks, controls, and performance metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of risk management efforts. This includes conducting risk assessments, control evaluations, and performance monitoring activities to measure the impact of AI risks on organizational objectives and stakeholder interests. Measurement helps organizations identify areas for improvement, track progress over time, and demonstrate the effectiveness of AI risk management practices to stakeholders. It may also involve benchmarking against industry standards or best practices to identify areas for improvement and drive continuous improvement.
Manage
Management in the NIST AI RMF refers to the implementation of risk management strategies, controls, and mitigation measures to address identified AI-related risks effectively. This includes implementing selected controls, developing risk treatment plans, and monitoring AI systems' security posture and performance. Management activities involve coordinating cross-functional teams, communicating with stakeholders, and adapting risk management practices based on changing risk environments. Effective risk management helps organizations minimize the impact of AI risks on organizational objectives, stakeholders, and operations while maximizing the benefits of AI technologies.
Key Components of the Framework
The NIST AI RMF consists of two primary components:
Foundational Information
This part includes introductory materials, background information, and context-setting elements that provide an overview of the framework's purpose, scope, and objectives. It may include definitions, principles, and guiding principles relevant to managing risks associated with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies.
Core and Profiles
This part comprises the core set of processes, activities, and tasks necessary for managing AI-related risks, along with customizable profiles that organizations can tailor to their specific needs and requirements. The core provides a foundation for risk management, while profiles allow organizations to adapt the framework to their unique circumstances, addressing industry-specific challenges, regulatory requirements, and organizational priorities.
Significance of AI RMF Based on Roles
Benefits for Developers
- Guidance on risk management: The AI RMF provides developers with structured guidance on identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks associated with AI technologies.
- Compliance with standards and regulations: The AI RMF helps developers ensure compliance with relevant standards, regulations, and best practices governing AI technologies. By referencing established NIST guidelines, such as NIST SP 800-53, developers can identify applicable security and privacy controls for AI systems.
- Enhanced security and privacy: By incorporating security and privacy controls recommended in the AI RMF, developers can mitigate the risks of data breaches, unauthorized access, and other security threats associated with AI systems.
- Risk awareness and mitigation: The AI RMF raises developers' awareness of potential risks and vulnerabilities inherent in AI technologies, such as data quality issues, model bias, adversarial attacks, and algorithmic transparency.
- Cross-disciplinary collaboration: The AI RMF emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between developers, cybersecurity experts, data scientists, ethicists, legal professionals, and other stakeholders in managing AI-related risks.
- Quality assurance and testing: The AI RMF encourages developers to incorporate risk management principles into the testing and validation processes for AI systems.
Benefits for Architects
- Designing secure and resilient systems: Architects play a crucial role in designing the architecture of AI systems. By incorporating principles and guidelines from the AI RMF into the system architecture, architects can design AI systems that are secure, resilient, and able to effectively manage risks associated with AI technologies. This includes designing robust data pipelines, implementing secure APIs, and integrating appropriate security controls to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
- Ensuring compliance and governance: Architects are responsible for ensuring that AI systems comply with relevant regulations, standards, and organizational policies. By integrating compliance requirements into the system architecture, architects can ensure that AI systems adhere to legal and ethical standards while protecting sensitive information and user privacy.
- Addressing ethical and societal implications: Architects need to consider the ethical and societal implications of AI technologies when designing system architectures. Architects can leverage the AI RMF to incorporate mechanisms for ethical decision-making, algorithmic transparency, and user consent into the system architecture, ensuring that AI systems are developed and deployed responsibly.
- Supporting continuous improvement: The AI RMF promotes a culture of continuous improvement in AI risk management practices. Architects can leverage the AI RMF to establish mechanisms for monitoring and evaluating the security posture and performance of AI systems over time.
Comparison of AI Risk Frameworks
|
Framework
|
Strengths
|
Weaknesses
|
|---|---|---|
|
NIST AI RMF
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AI Ethics Guidelines from Industry Consortia
|
|
|
Conclusion
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework offers a comprehensive approach to addressing the complex challenges associated with managing risks in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. Through its foundational information and core components, the framework provides organizations with a structured and adaptable methodology for identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks throughout the AI lifecycle. By leveraging the principles and guidelines outlined in the framework, organizations can enhance the security, reliability, and ethical use of AI systems while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations. However, it's essential to recognize that effectively managing AI-related risks requires ongoing diligence, collaboration, and adaptation to evolving technological and regulatory landscapes. By embracing the NIST AI RMF as a guiding framework, organizations can navigate the complexities of AI risk management with confidence and responsibility, ultimately fostering trust and innovation in the responsible deployment of AI technologies.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments