Jenkins vs. Bamboo: Battle Of The Best CI/CD Tools
Bamboo and Jenkins are two of the leading continuous integration tools by developers, Explore this comparison between them in terms of ease of use and more.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeJenkins and Bamboo are leading automation servers with plugins built for continuous integration. So before using them in your DevOps lifecycle, you must understand what exactly they are and how they work. To understand, read this article which talks about the usability face-off between Jenkins and Bamboo.
Before, we look into the differences between Jenkins and Bamboo, let us understand the basics of Jenkins and Bamboo.
What Is Bamboo?
Bamboo is an automation server used for continuous integration. Developed by Atlassian in 2007, this tool allows the developers to automatically build, document, integrate, test the source code, and prepare an app for deployment. It comes with the flexibility to use various tools, an easy-to-use graphical user interface, and allows the developers to use CI/CD methodologies.
With Bamboo, you can ensure high quality and status, get end-to-end visibility into release implementation, and spend maximum time writing the code rather than integrating various software. It also provides built-in deployment support, powerful build agent management, automated merging, and built-in Git branch workflows.
Related: Continuous integration and delivery for database changes.

Next, let us understand the basics of Jenkins.
What Is Jenkins?
Jenkins is one of the most popular tools in today’s market, built for continuous integration purposes. Written in Java, Jenkins is used to build and test software projects and makes it easy for developers to integrate the required changes to the project. This tool also aims to continuously deliver software by integrating a large number of testing and deployment software.
By using Jenkins, startups and hyper-growth companies can accelerate the software development process through automation. Also, Jenkins integrates the development life-cycle process of different kinds such as build, document, test, package, stage, deploy, static analysis, and much more. It provides various plugins to allow integration of various DevOps stages. For example, if you want to use a particular tool, then you just need to install the required plugins for that particular tool.
Refer to the image below to understand the role of Jenkins in various DevOps stages:
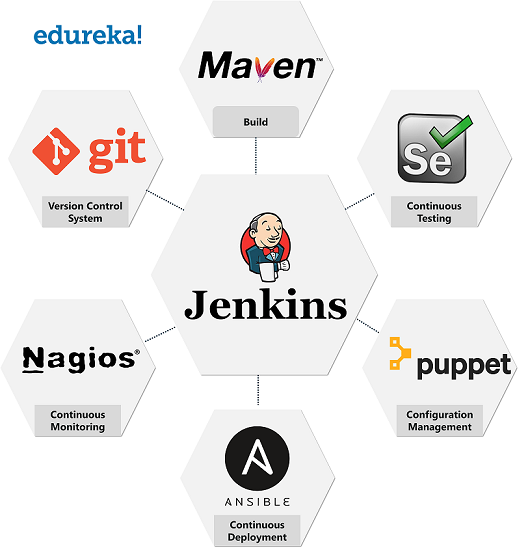
Now that you know more about Jenkins and Bamboo, let us see how these tools stand against each other.
The differences between Jenkins vs. Bamboo are briefly summarized in the below table. A detailed explanation is provided later in the article.
| Features | Jenkins | Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Popularity | More popular than Bamboo |
Less Popular than Jenkins |
| License Terms | Open Source | Commercial Software |
| Origin | Java Programming Language | Java Programming Language |
| Ease of Setup | Easy to setup | Slightly Complicated |
| User-Friendly | Less user-friendly | More user-friendly |
| Documentation | Provides good online documentation | Provides good online documentation |
| Platform Dependency |
|
|
| Support | Has good community support | Provides support for licensed users |
| Plugin Support | Has 1000+ plugins to integrate with various platforms |
Has fewer plugins compared to Jenkins |
| Compatibility |
|
|
Jenkins vs Bamboo
In this face-off on Jenkins vs Bamboo, I will be comparing both these tools based on the following grounds:
- Popularity
- License Terms
- Origin
- Ease of Setup
- User-friendly
- Documentation
- Platform Dependency
- Support
- Plugins Support
- Compatibility
Popularity
On comparing these tools based on popularity, Jenkins definitely wins and is much more popular than Bamboo. Jenkins was released much earlier than Bamboo, and it immediately started gaining popularity among organizations.
Also, if you look at the current Google Trends of these tools, you will clearly observe that Jenkins is much ahead in the competition. Jenkins continues to dominate the market looking for a solution to build a continuous delivery pipeline as it has more than 165,000 active installations.
License Terms
Jenkins is an open-source tool, whereas Bamboo is a commercial/licensed tool. Jenkins has a global community for development, but Bamboo has its own team of dedicated development. So, any individual or professional working in the DevOps field can go and download Jenkins.
However, to use Bamboo you can download the free version available for 30 days. After that, you have to buy the license for $10 which provides 10 jobs, unlimited local agents, and no remote agents, or for $1,270 which provides unlimited jobs and local agents. Here, remember that the higher of a plan you have, the more agents you will require. Otherwise, you will risk creating a process and slowing down the process.
Origin
Well, the origin of both tools is the programming language Java. Jenkins was developed as the Hudson project in 2004 by Kohsuke Kawaguchi and was first released in java.net in 2005.
Similarly, while developing Bamboo, Atlassian decided to use a simple Java-based plan description language to ensure syntax checks, code auto-completion, validate code, and run offline tests. In Bamboo, you can write your code in any JVM language, which incorporates Java-like Groovy, Scala, or Kotlin. Do not have to worry, if you are not familiar with Java, both these tools will bootstrap you directly into a working environment with the help of the documentation available.
Ease of Setup
Both of these tools are quite easy to install and configure. They can be configured with a snap of your fingers. However, if we still have to choose the better of them, then I would say Jenkins stands out, as it can be done in three steps if Java and Apache Tomcat are already installed. You have to download the Jenkins war file from the official website, deploy the war file, and then install the required/suggested plugins.
However, to set up Bamboo, you need to few more steps when compared to Jenkins. Here, after installing Java and creating a dedicated user to run Bamboo, you have to:
- Download Bamboo
- Create an installation directory
- Create the home directory
- Start Bamboo
- Configure Bamboo
User-Friendly
When it comes to user-friendliness, Jenkins is not a great contender here. This is because Bamboo has a user-friendly approach with a neat and intuitive user interface. So, every time a new task is added, it provides proper guidance throughout the plan’s build and deployment states.
But, when it comes to Jenkins, this tool is completely based on functionality. So, if you wish to make the Jenkins platform more intuitive, then you need to work on it. However, some would say this leaves room for the developers to customize and create, allowing the developers to choose from a variety of plugins.
Documentation
Jenkins and Bamboo both have fantastic online documentation that offers clients the option to research and find a solution before reaching support for help.
In this documentation, you will find all the information related to the tools such as how to install them, prerequisites, steps to perform a task, commands, etc. Documentation also provides various tutorials to help you gain hands-on experience with the tool.
Platform Dependency
Jenkins and Bamboo work on various platforms and can be integrated with various tools. The following are the different operating systems and browsers Jenkins and Bamboo can work on.
Jenkins
- Works on operating systems such as Windows, Ubuntu, RedHat, and MacOS
- It can be used on browsers such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Internet Explorer.
Bamboo
- Works on operating systems such as Windows, Linux, Solaris
- It can be used on browsers such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
Jenkins vs Bamboo: Support
Jenkins offers global community support to users who are facing issues while using Jenkins. But Bamboo offers great professional support for licensed customers. It also has detailed online documentation available.
Apart from this, Bamboo gets support from the Atlassian community. So my take on this point is that both of them do offer support, but I would say there is a difference between the types of help offered by these tools.
Plugin-Support
Jenkins dominates this field and offers more than 1,000 plugins that enable Jenkins to integrate with any tool like Git, Maven 2, Amazon EC2, and HTML publisher. These plugins enable the user to give the best of solutions throughout the continuous delivery process. Even if a plugin does not exist, you can code it and share it with the community.
But, Bamboo is not the leader here. Bamboo has around only 100 plugins in the Atlassian environment, as most of the features are built in the Bamboo marketplace. However, this tool easily integrates with Jira and Bitbucket when compared to Jenkins.
Compatibility
| Jenkins | Bamboo |
|---|---|
Does not support built-in JIRA software integration |
Supports built-in JIRA software integration |
Does not support built-in Git branching workflows |
Supports built-in GIT software integration |
Does not support built-in BitBucket server integration |
Supports built-in BitBucket server integration |
Supports built-in deployment projects |
Supports built-in deployment projects |
Supports REST API |
Supports REST API |
Supports test automation via plugins |
Supports test automation |
Supports enterprise-grade permissions via plugins |
Supports enterprise-grade permissions |
Which CI/CD Tool Should You Choose?
As I have already mentioned, both tools are prominent in the DevOps field and hold paramount importance. So, you can opt for either of the two. But before you choose your tool, there are a few important aspects that you need to consider like:
- Support and management offered by tools
- User interface and integration support
- Type of systems such as standalone systems and large software systems
In short, I would say it is your choice which tool you want to choose based on your requirements in the DevOps lifecycle. So, these are the relevant parameters you have to keep in mind before choosing between Jenkins and Bamboo. I hope you found this article informative.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments