REST API — What Is HATEOAS?
In this article, continue to learn about REST APIs and learn about HATEOAS.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
While viewing a web page, you can see data on the page and perform actions with it. How about a REST API? Typically, when you ask for a REST resource, you get the details of the resource back. How about sending the operations that you can do with the resource in the response?
You might also like: RESTful Web Services With Spring Boot, Gradle, HATEOAS, and Swagger
We Learn
- What is HATEOAS?
- Why do you need to use HATEOAS?
- When do you make use of HATEOAS?
REST API
This is the fifth article in a series of articles on REST APIs:
- 1 - Introduction to REST API — RESTful Web Services
- 2 - REST vs SOAP — A Few Perspectives
- 3 - Designing a REST API — What Is Contract First?
- 4 - Designing a REST API — What Is Code First Approach?
What Does HATEOAS Stand For?
The term HATEOAS stands for the phrase Hypermedia As The Engine Of Application State. To understand this further, we first need to understand the meaning of Hypermedia.
Have a look at the following web page:
When the browser loads the page, you definitely can see all the content that the page has to offer. More interestingly, the page also allows you to perform a lot of actions around that data, such as:
- Clicking on buttons (the green "Clone or Download")
- Clicking on tabs (to view the "Issues", for instance)
- and several more
Now let's look at how our REST API's behave:
If you look at a typical GET request to a RESTful server, such as this one:
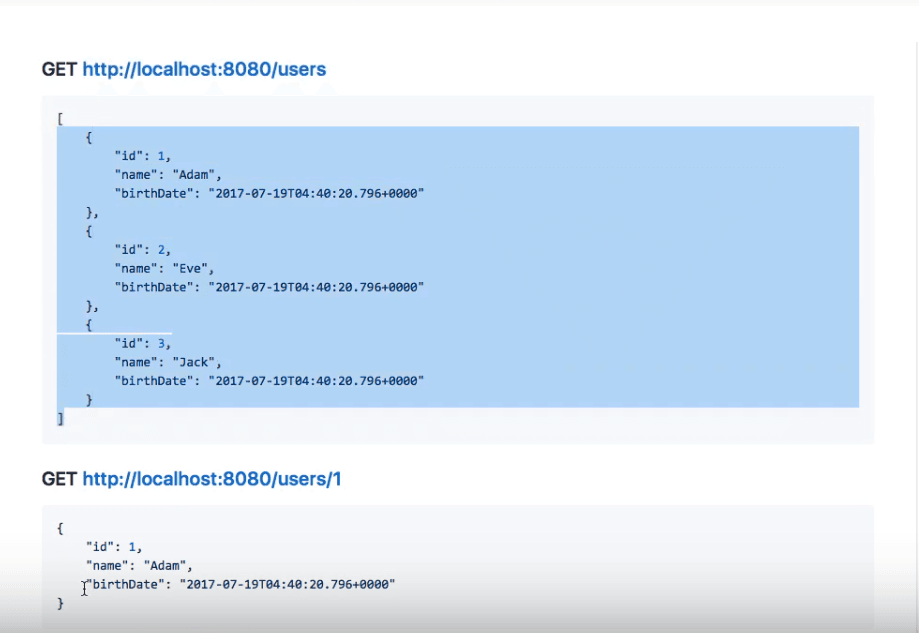
The request to GET http://localhost:8080/users retrieves a set of three users' details in this case. Sending a request with GET http://localhost:8080/users/1 will retrieve details of just the first user.
Typically, when we perform a REST request, we only get the data and not any actions around it. This is where HATEOAS comes in the fill in the gap.
A HATEOAS request allows you to not only send the data but also specify the related actions:
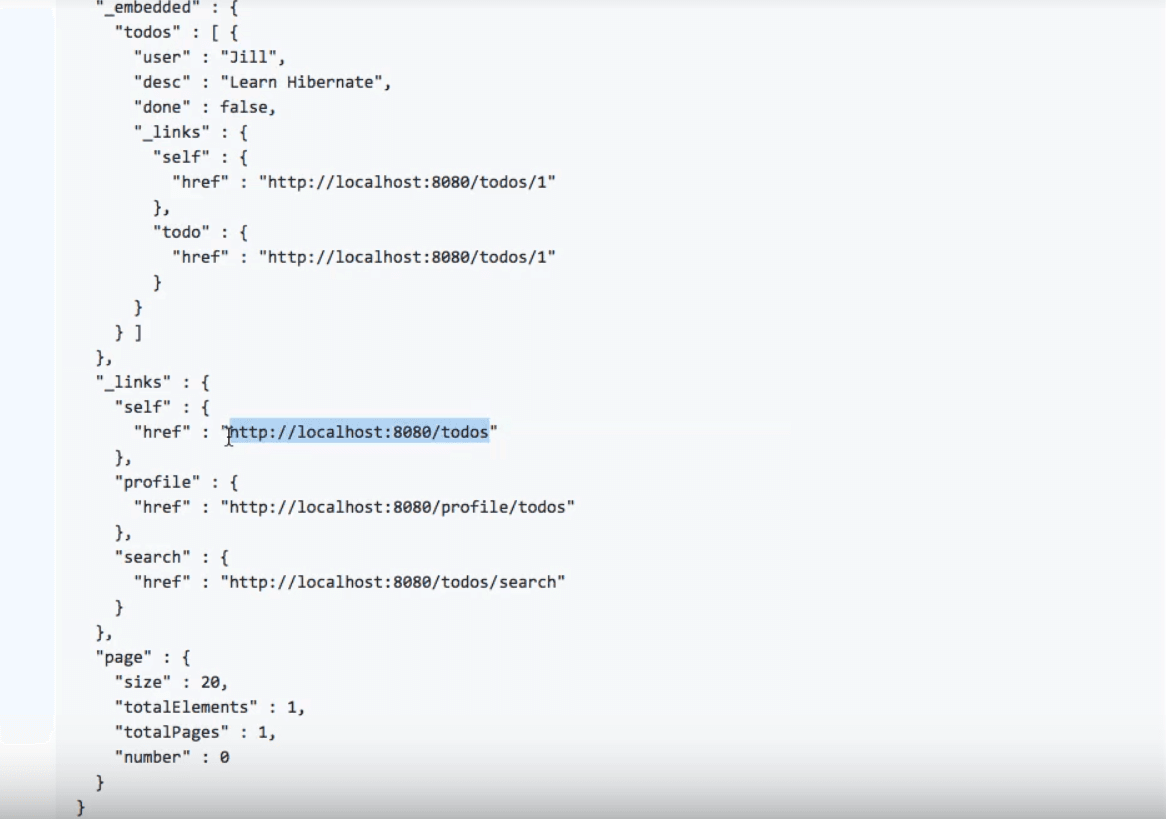
This example was in the JSON format. An XML format for another example would look something like this:
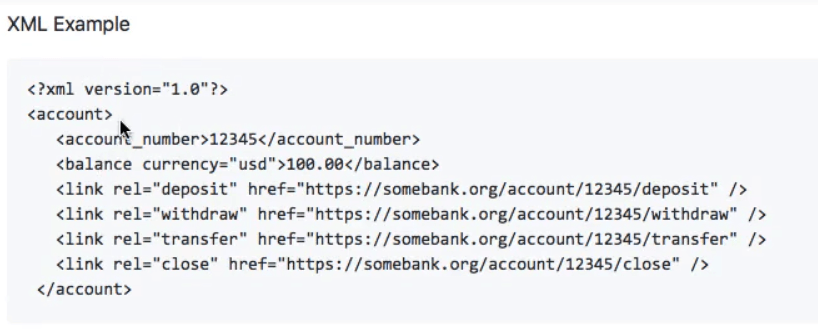
When you send out this request to retrieve account details, you get both:
- Account number and balance details
- Links that provide actions to do a deposit/withdrawal/transfer/closure
With HATEOAS, a request for a REST resource gives me both data, and actions related to the data.
Why Do We Need HATEOAS?
The single most important reason for HATEOAS is loose coupling. If a consumer of a REST service needs to hard-code all the resource URLs, then it is tightly coupled with your service implementation. Instead, if you return the URLs, it could use for the actions, then it is loosely coupled. There is no tight dependency on the URI structure, as it is specified and used from the response.
A few significant topics related to HATEOAS are:
HAL — Hypertext Application Language
When you design a RESTful service, there is a need to specify how to return data and links corresponding to a request. HAL is a simple format that gives an easy, consistent way to hyperlink between resources in your REST API. Here is an example:

With HAL, you have a few categories of representations:
- Links:Specified as a combination of
- Target — Given as a URI
- Relation — A name
- Embedded Resources: Other resources contained within a given REST resource
- State: The actual resource data
If you happen to use the Spring Framework to develop your REST service, then Spring HATEOAS is a good engine to use for your service.
Check out our video on this:
Summary
In this article, we looked at what HATEOAS stands for. With HATEOAS, responses to REST requests return not just the data, but also actions that can be performed with the resource. This helps in making the applications loosely coupled.
Further Reading
Published at DZone with permission of Ranga Karanam, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments