The Art of Ethical Hacking: Securing Systems in the Digital Age
Ethical hacking utilizes techniques for positive purposes, safeguarding digital systems from cyber threats by identifying vulnerabilities before malicious hackers.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn today’s world, where everything is connected to the internet, cybersecurity is more significant than ever. Cyberattacks can cause serious damage to individuals, businesses, and governments by stealing data, disrupting services, or compromising systems. To prevent these attacks, we must understand how hackers think and operate and how to safeguard ourselves against them. This is where ethical hacking comes in. In this article, we will be discussing the art of ethical hacking and how it can help safeguard systems in the digital age.
Ethical Hacking
Ethical hacking can be portrayed as a controlled and authorized endeavor to exploit system vulnerabilities and identify flaws before malevolent actors may make use of them. Assessing a system, network, or application’s security posture is the principal objective. By taking a proactive stance, organizations can stop data breaches, financial losses, and reputational harm by spotting and fixing possible security vulnerabilities before they are utilized against them.
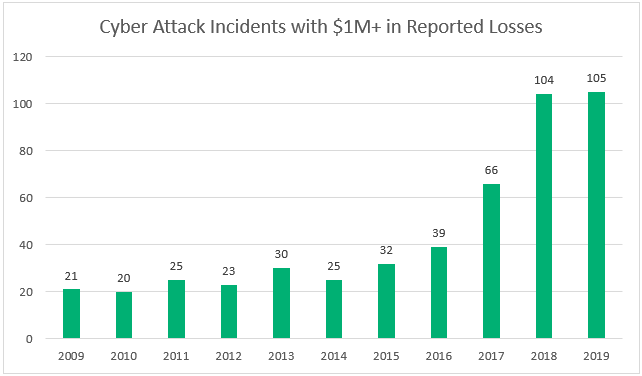
Over the past 10 years, there have been various occurrences of cyber attack trends we’ve seen come and go. Some are very consistent in terms of being counted annually. For instance, one such cyber security attack statistic that we’re able to track from year to year is the number of cyber attacks that result in reported losses that exceed $1 million.
The Center for Strategic & International Studies (CSIS) tracks “cyber attacks on government agencies, defense, and high tech companies, or economic crimes with losses of more than a million dollars.” In the last ten years, they’ve tracked 490 crucial cyber incidents.
Ethical Hacking and Malicious Hacking
Stressing the obvious differences between malicious hacking and ethical hacking is vital. Even though the strategies utilized could be comparative, ethical hacking is carried out with permission and aims to strengthen security. On the other hand, malicious hacking entails unlawful admittance to steal, disrupt, or manipulate data without authorization. Operating within moral and legal bounds, ethical hackers make sure that their acts advance cybersecurity measures as a whole.
Ethical hacking is the term used to describe a legitimate attempt to obtain unauthorized access to a computer system, program, or information. Ethical hacking includes imitating the methods and actions of vicious attackers. By using this method, security vulnerabilities can be found and fixed before a malicious attack can make use of them.
Ethical Hackers Skills
A thorough awareness of cybersecurity principles, technological proficiency, and inventiveness are important for ethical hacking. This section explores the fundamental talents and resources that ethical hackers frequently use to find weaknesses and fortify digital defenses.
- Networking knowledge: Understanding networking principles thoroughly is essential. Understanding network data flow and spotting possible weak spots in routers, switches, and other network components are essential skills for ethical hackers.
- Operating system familiarity: Having various operating system skills, ethical hackers can use Linux, Windows, and macOS. This understanding is essential for assessing and safeguarding diverse environments.
- Programming skills: Programming languages like Python, Java, or C+-+ are the programming skills used by ethical hackers. This allows them to fathom and manipulate the underlying code of applications and systems.
Tools Commonly Used in Ethical Hacking
- Exploitation frameworks: To test and exploit vulnerabilities in a controlled environment, ethical hackers utilize frameworks such as Metasploit to mimic cyber-attacks.
- Password cracking tools: Ethical hackers use various tools to crack passwords using different techniques. Tools like John the Ripper or Hascat assist ethical hackers in evaluating the security of passwords.
- Vulnerability scanners: Ethical hackers use various tools to automatically find and evaluate vulnerabilities in networks, systems, or applications; ethical hackers utilize programs like OpenVAS or Nessus.
- Packet sniffers: Examples of packet sniffers used to record and examine network traffic include Tepdump and Wireshark, which help ethical hackers locate possible security flaws.
Types of Hackers
Hackers are frequently categorized using the analogy of wearing different “hats” based on their behaviors and objectives. By the color of their figurative hats, the following are some of the most prevalent categories of hackers.
- White hat hackers: Legal hacking is what white hat hacking does to increase users’ digital security. They are compensated for breaking into digital systems to detect possible security flaws and report back to their clients. By utilizing white hat hacking, businesses and organizations can fix security flaws before malevolent hackers can take advantage of them.
- Black hat hackers: Cybercriminals who use evil intentions to illegally breach networks are known as black hat hackers. The goal of black hat hacking is to obtain unauthorized access to computer systems. When a security flaw is discovered by a black hat hacker, they try to take advantage of it, often by implanting a virus or other type of malware such as trojan.
- Grey hat hackers: Gray hat hackers might not have the same illegal or harmful intentions as black hat hackers, but they also lack the prior knowledge or approval of people whose systems they hack into. However, instead of completely exploiting vulnerabilities like zero-day ones, gray hat hackers report them when they find them. Grey hat hackers, however, can request payment in exchange before revealing all the information they discovered.
- Red hat hackers: Red hats, also referred to as vigilante hackers, take strong actions to thwart black hats and utilize some of their strategies. Red hats are employed by government organizations to support their missions.
- Blue hat hackers: Blue hat hackers can also be referred to as white hat hackers who are employed and authorized by an organization. Their duties are to safeguard the cybersecurity of the organization and stop attacks. When blue hats start working for a company or organization, they are typically not referred to as hackers. Blue hats may not be responsible for carrying out hacks alone; instead, they frequently operate in teams. They normally work for large companies' IT departments.
The Future of Ethical Hacking
As everybody and organizations keep on depending on technology for everyday tasks and business operations, the role of ethical hacking in strengthening cybersecurity will only become more crucial. A safe digital environment can be the difference between one that is susceptible to potentially catastrophic cyberattacks and one that embraces ethical hacking as a proactive strategy. There are a lot of difficulties ahead for ethical hackers. They will need to contend with AI-driven attacks, quantum computing threats, and the constant evolution of hacking procedures. Staying ahead of these challenges requires a commitment to ongoing training and adaptation.
Conclusion
The field of ethical hacking has solidified itself as a crucial component of cybersecurity. However, it continues to evolve, and this has led to much discussion about the best model that should be utilized. Ethical hacking can assist in a variety of ways as it improves computer and network security by performing penetration testing; it allows one to take preventive actions to avoid any security breach situation. Ethical hackers are the silent guardians of our digital world, working vigorously to keep us safe in the digital realm.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments