How To Implement OAuth2 Security in Microservices
Learn to implement OAuth2 Security in microservices distributed systems using OAuth2, Oauth2-Client, Spring Cloud, and Netflix components with full examples.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhat Is OAuth2?
OAuth 2.0 is an authorization protocol. It provides the framework to obtain limited access to a protected resource by a third-party application on behalf of the resource owner. For example, we log in to our LinkedIn account using Google account username and password. The Google authorization (OAuth2.0) server grants a temporary access token to LinkedIn which authorizes the user to access LinkedIn resources. Note that here, LinkedIn trusts Google to validate the user and acts as an authorization proxy.
What Are Microservices?
A microservice is a service-oriented architecture pattern wherein applications are built as a collection of various smallest independent service units. It is a software engineering approach that focuses on decomposing an application into single-function modules with well-defined interfaces. These modules can be independently deployed and operated by small teams who own the entire life-cycle of the service.
Why Is OAuth2 a Good Solution for Secure Communications With Microservices?
- This idea of separation of concern leverages microservices security by decoupling the part that does authorization from business logic. The responsibility is delegated to a centralized and trusted authorization server and the actual application is free from security concerns in this regard.
- It promotes the granularity of service which microservices typically are all about. Apart from reducing complexity, OAuth 2.0 in microservices provides a platform to implement consistent and standard security policies across the system.
- The authorization is flexible, meaning it can be revoked at any time. This helps security management to restrict unnecessary or limited access to resources.
- Since access tokens provided by the OAuth 2.0 server are stateless (JSON Web Token - JWT), it eliminates the need for storage and transmission of sensitive credentials or session data between microservices.
- Overall, both (OAuth 2.0 and microservices) in combination enhance the performance and scalability of the system.
Purpose
I wanted a solution where we could easily capture OAuth2 and OAuth2 clients for secure communication with all of the microservices, focusing on how to achieve OAuth2 full flavor in a microservices architecture. The user can’t access API without a token. The token will be available when the user is given basic authentication details to generate a token for access API.
All requests will consider one entry point (API Gateway), but service-to-service can communicate. The API Gateway will use dynamic routing with the Zuul Netflix OSS component. Every request will check authorization when the request arrives in the service, and the service will request the authorization server to verify if it is either authenticated or not. The entire Meta configuration settled into the central configuration on GitHub (you can manage it on any repository).
Goal
- Achieve authentication/authorization, based on Spring Security, OAuth2, and OAuth2 client
- Understanding microservices architecture using Spring Cloud and Netflix OSS
- Demonstration of microservice architecture based on Java, Spring, and OAuth2
Spring Cloud and Microservices
Firstly, we do not write a microservice. We write a service that eventually will be called microservice when deployed with other services to form an application.
Having said that, Spring Cloud just gives you abstractions over some set of tools (Eureka, Zuul, Feign, Ribbon, etc.), making it easy for you to integrate with spring applications.
However, you can also achieve microservice architecture without using Spring Cloud. You can take advantage of tools like Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, HAProxy, Kong, NGINX, etc. to achieve the same. Using Spring Cloud has its own pros and cons and vice versa.
High-Level Microservice Architecture With Authorizations

- Users log in to the system using basic authorization and login credentials. The user will get a token if the user's basic auth and login credentials are matched.
- Next, the user sends a request to access data from the service. The API gateway receives the request and checks with the authorization server.
- Every request has one entry point API Gateway.
- Security checking and dynamic routing to the service
- Every service has a single database to manipulate data.
Spring Cloud Key Concept and Features
- Spring Cloud works for microservices to manage configuration.
- Intelligent routing and services discovery
- Service-to-service call
- Load balancing (it properly distributes network traffic to the backend server)
- Leadership election (the application works with another application as a third-party system)
- Global lock (two threads are not accessed simultaneously for the same resource at the same time)
- Distributed configuration and messaging
If you want to avail many services in one application, then the cloud-based application is an easy way. Spring Cloud works in the same way.
Spring Boot Key Concept and Features
- Spring Boot works to create microservices.
- Spring application creates a stand-alone Spring application.
- Web application HTTP embedded (Tomcat, Jetty, or Undertow); no need to deploy WAR file
- Externalized configuration
- Security (it is secure inbuilt with basic authentication on all HTTP endpoints)
- Application event and listener
- Spring Boot works on product-based web applications. It is used for unit test development and integration test time reduction.
Spring Cloud Advantages
- Provides cloud service development
- Microservice-based architecture and configuration
- Provides inter-service communication
- Based on the Spring Boot model
Spring Cloud 5 Main Annotations
1. @EnableConfigServer
This annotation converts the application into a server which more applications use to get their configuration.
2. @EnableEurekaServer
This annotation is used for Eureka Discovery Services for other applications that can be used to locate services using it.
3. @EnableDiscoveryClient
This annotation helps an application register in the service discovery and discover other services using it.
4. @EnableCircuitBreaker
Use the circuit breaker pattern to continue operating when related services fail and prevent cascading failure. This annotation is used for Hystrix Circuit Breaker.
5. @HyStrixCommand(fallbackmethod="MethodName")
Hystrix is a latency and fault tolerance library for distributed systems.
4 Common Netflix Components
Spring Cloud Netflix provides Netflix OSS integrations for Spring Boot apps through autoconfiguration and binding to the Spring Environment and other Spring programming model idioms. With a few simple annotations, you can quickly enable and configure the common patterns inside your application and build large distributed systems with battle-tested Netflix components. The patterns provided include Service Discovery (Eureka), Circuit Breaker (Hystrix), Intelligent Routing (Zuul), and Client-Side Load Balancing (Ribbon).
1. Eureka (Service Registration and Discovery)
- REST service which registers itself at the registry (Eureka Client)
- Web application, which is consuming the REST service as a registry-aware client (Spring Cloud Netflix Feign Client)
2. Ribbon (Dynamic Routing and Load Balancer)
- Ribbon primarily provides client-side load-balancing algorithms.
- APIs that integrate load balancing, fault tolerance, caching/batching on top of other Ribbon modules and Hystrix
- REST client built on top of Apache HttpClient integrated with load balancers (deprecated and being replaced by ribbon module
- Configurable load-balancing rules
3. Hystrix (Circuit Breaker)
Hystrix is a fault-tolerance Java library. This tool is designed to separate points of access to remote services, systems, and 3rd-party libraries in a distributed environment like microservices. It improves the overall system by isolating the failing services and preventing the cascading effect of failures.
4. Zuul (Edge Server)
- Zuul is the front door for all requests from devices and websites to the backend of the Netflix streaming application.
- Zuul will serve as our API gateway.
- Handle dynamic routing
- Built to enable dynamic routing, monitoring, resiliency, and security
What Is a Feign Client?
Netflix provides Feign as an abstraction over REST-based calls, by which microservices can communicate with each other, but developers do not have to bother about REST internal details.
Feign Client, which works on the declarative principle. We must create an interface/contract, then Spring creates the original implementation on the fly, so a REST-based service call is abstracted from developers. Not only that — if you want to customize the call, like encoding your request or decoding the response in a custom object, you can do it with Feign in a declarative way. Feign, as a client, is an important tool for microservice developers to communicate with other microservices via Rest API.
The Feign Client uses a declarative approach for accessing the API. To use it, we must first enable the Spring Cloud support for it on our Spring Boot Application with the @EnableFeignClients annotation at the class level on a @Configuration class.
Server Side Load Balancing
In JavaEE architecture, we deploy our WAR/EAR files into multiple application servers, then we create a pool of servers and put a load balancer (Netscaler) in front of it, which has a public IP. The client makes a request using that public IP, and Netscaler decides in which internal application server it forwards the request by round robin or sticky session algorithm. We call it server-side load balancing.
Technology Stack
- Java 8+
- Spring latest
- Spring Security
- OAuth2, OAuth2 Client
- Spring Cloud
- Netflix OSS
- PostgreSQL
- IntelliJ
How To Implement OAuth2 Security in Microservices

Step 1: Create Project "central configuration" for All Services
With microservices, we create a central config server where all configurable parameters of microservices are written and version-controlled. The benefit of a central config server is that if we change a property for a microservice, it can reflect that on the fly without redeploying the microservice.
You can create a project using spring initializr.
application.properties:
xxxxxxxxxx
spring.application.name=ehealth-central-configuration
server.port=8888
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
# available profiles of the application
spring.profiles.active=local,development,production
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri=https://github.com/amran-bd/cloud-config
spring.cloud.config.server.git.clone-on-start=true
spring.cloud.config.server.git.search-paths=patient-management-service,ehealth-api-gateway,eureka-service-discovery,clinic-management-service
management.security.enabled=false
#To remove WAR - Could not locate PropertySource: None of labels [] found
health.config.enabled=false
# To remove I/O Issue Could not locate PropertySource: I/O error on GET request for
spring.cloud.config.enabled=false
Hint: You can use your Git server or local machine. A new service name will be added if a new service is introduced.
Here is the link to my GitHub repository if you would like to use it.
EhealthCentralConfigurationApplication.Java Class Example:
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.amran.central.config;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
public class EhealthCentralConfigurationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EhealthCentralConfigurationApplication.class, args);
}
}
You must include an annotation @EnableConfigServer.
Example of Creating a Central Configuration for Services:

Hint: Create folder <projectName>/<projectName-development.properties>.
Step 2: Create a Project "Discovery Server" for All Discoverable Services
We have already discussed the discovery server in this article.
bootstrap.properties:
xxxxxxxxxx
spring.application.name=eureka-service-discovery
spring.profiles.active=development
# ip and port of the config server
spring.cloud.config.uri=http://localhost:8888
# expose actuator endpoints
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=refresh
management.security.enabled=false
spring.cloud.config.fail-fast=true
Here, we can enable and disable other actuator endpoints through property files.
If you want to enable all actuator endpoints, then add the following property:management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*. To enable only specific actuator endpoints, provide the list of endpoint IDs:
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=health,info,beans,env
In some cases, it may be desirable to fail the startup of a service if it cannot connect to the Config Server. If this is the desired behavior, set the bootstrap configuration property spring.cloud.config.fail.Fast=true and the client will halt with an exception.
EurkeaServiceDiscoveryApplication.java Class Example:
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.amran.service.discovery;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
public class EurekaServiceDiscoveryApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServiceDiscoveryApplication.class, args);
}
}
You must include an annotation @EnableEurekaServer.
Step 3: Create Project "API Gateway" for All Services Entry Points
This is the most valuable portion. Here, we write the authorization server in the same project.
API Gateway Project Structure

application.yml
xxxxxxxxxx
#hystrix:
# command:
# default:
# execution:
# isolation:
# thread:
# timeoutInMilliseconds: 5000
hystrix:
command:
clinic-management-service:
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 5000
patient-management-service:
execution:
isolation:
thread:
timeoutInMilliseconds: 5000
Here, define timeout for every separate service; you can use the default.
bootstrap.properties
xxxxxxxxxx
spring.application.name=ehealth-api-gateway
spring.profiles.active=development
# ip and port of the config server
spring.cloud.config.uri=http://localhost:8888
# expose actuator endpoints
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=refresh
management.security.enabled=false
spring.cloud.config.fail-fast=true
Central Configuration Example
ehealth-api-gateway-development.properties:
x
spring.application.name=ehealth-api-gateway
server.port=8080
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka/
## PostgreSQL
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:3307/ehealth-security
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=test1373
spring.datasource.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
# Hikari will use the above plus the following to setup connection pooling
spring.datasource.hikari.minimumIdle=3
spring.datasource.hikari.maximumPoolSize=500
spring.datasource.hikari.idleTimeout=30000
spring.datasource.hikari.poolName=SpringBootJPAHikariCP
spring.datasource.hikari.maxLifetime=2000000
spring.datasource.hikari.connectionTimeout=30000
spring.datasource.pool-prepared-statements=true
spring.datasource.max-open-prepared-statements=250
spring.jpa.hibernate.connection.provider_class=org.hibernate.hikaricp.internal.HikariCPConnectionProvider
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQL82Dialect
#Hibernate Configuration
spring.jpa.generate-ddl = true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
server.error.include-stacktrace=never
#feign.hystrix.enabled=true
#hystrix.shareSecurityContext=true
#All url come with prefix/api will interpret
zuul.prefix=/api
#Dynamic Service Registration in Eureka Server (API Gateway)
zuul.routes.patient-management-service.path=/patient-management-service/**
#zuul.routes.patient-management-service.url=http://localhost:8081
zuul.routes.patient-management-service.sensitive-headers
zuul.routes.patient-management-service.service-id=patient-management-service
zuul.routes.clinic-management-service.path=/clinic-management-service/**
#zuul.routes.patient-management-service.url=http://localhost:8082
zuul.routes.clinic-management-service.sensitive-headers
zuul.routes.clinic-management-service.service-id=clinic-management-service
Zuul filtered 4-types while doing dynamic routing.
Zuul filters store request and state information in (and share it using) the RequestContext. You can use that to get to the HttpServletRequest and then log the HTTP method and URL of the request before it is sent on its way.
ErrorFilter, PreFilter, PostFilter, and RouteFilter
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.amran.api.gateway.filter;
import com.netflix.zuul.ZuulFilter;
/**
* @Author : Amran Hosssain on 6/27/2020
*/
public class RouteFilter extends ZuulFilter {
public String filterType() {
return "route";
}
public int filterOrder() {
return 1;
}
public boolean shouldFilter() {
return true;
}
public Object run() {
System.out.println("Inside Route Filter");
return null;
}
}
EhealthApiGatewayApplication.java Class Example
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.amran.api.gateway;
import com.amran.api.gateway.filter.PostFilter;
import com.amran.api.gateway.filter.PreFilter;
import com.amran.api.gateway.filter.ErrorFilter;
import com.amran.api.gateway.filter.RouteFilter;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.EnableCircuitBreaker;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.EnableZuulProxy;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
public class EhealthApiGatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EhealthApiGatewayApplication.class, args);
}
public PreFilter preFilter() {
return new PreFilter();
}
public PostFilter postFilter() {
return new PostFilter();
}
public ErrorFilter errorFilter() {
return new ErrorFilter();
}
public RouteFilter routeFilter() {
return new RouteFilter();
}
}
AsEhealthApiGatewayApplication.java class annotation has been already discussed, see above if it is not clear.
Spring Security and Oauth2 Implementation in Microservices Architecture

I have done OAuth2 implementation based on Spring Security.
Step 4: Create a Project "patient-management-service"
Patient-related data will be manipulated.
POM.xml
xxxxxxxxxx
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.amran.patient.management</groupId>
<artifactId>patient-management-service</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>patient-management-service</name>
<description>patient-management-service project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.SR5</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security.oauth</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<resources>
<resource>
<filtering>true</filtering>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>*.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>
bootstrap.properties
x
server.url = Patient Management Service Working...
spring.application.name=patient-management-service
spring.profiles.active=development
# ip and port of the config server where we can get our central configuration.
spring.cloud.config.uri=http://localhost:8888
# expose actuator endpoints
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=refresh
management.security.enabled=false
spring.cloud.config.fail-fast=true
##Security parameter for request verification ##
#we consider basic authorization and Token. In auth server verified this token generated by authorization server (Self) based below criteria.
client_id=kidclient
client_credential = kidsecret
check_authorization_url = http://localhost:8080/oauth/check_token
resources_id = ehealth
PatientManagementServiceApplication.java Class Example
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.amran.patient.management;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
public class PatientManagementServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PatientManagementServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
You must annotate @EnableDiscoveryClient in the class so the Eureka server will be discovered as a service or client.
Security OAuth2-Client: ResourceServerConfig.java, WebSecurityConfig.Java Class Example
You need a WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter to secure the /authorize endpoint and to provide a way for users to authenticate. A Spring Boot application would do that for you (by adding its own WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter with HTTP basic auth). It creates a filter chain with order=0 by default and protects all resources unless you provide a request marcher.
The @EnableResourceServer does something similar, but the filter chain it adds is at order=3 by default. WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter has an @Order(100) annotation. So first the ResourceServer will be checked (authentication), and then your checks in your extension of WebSecurityConfigureAdapter will be checked.
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.amran.patient.management.security;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableResourceServer;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer;
/**
* @Author : Amran Hosssain on 6/27/2020
*/
public class ResourceServerConfig extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
("${resources_id}")
private String resourceId;
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.headers().frameOptions().disable()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/eureka/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated();
}
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) throws Exception {
resources.resourceId(resourceId);
}
}
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.amran.patient.management.security;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.authentication.OAuth2AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.RemoteTokenServices;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.token.ResourceServerTokenServices;
/**
* @Author : Amran Hosssain on 6/27/2020
*/
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
("${client_id}")
private String clientId;
("${client_credential}")
private String clientSecret;
("${check_authorization_url}")
private String checkAuthUrl;
public ResourceServerTokenServices tokenServices() {
RemoteTokenServices tokenServices = new RemoteTokenServices();
tokenServices.setClientId(clientId);
tokenServices.setClientSecret(clientSecret);
tokenServices.setCheckTokenEndpointUrl(checkAuthUrl);
return tokenServices;
}
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
OAuth2AuthenticationManager authenticationManager = new OAuth2AuthenticationManager();
authenticationManager.setTokenServices(tokenServices());
return authenticationManager;
}
}
Check How It Works
1. Generate Token
- Project run sequence:
- CentralConfigServer->DiscoveryServer->API Gateway Server-> Others Service

2. Client Details In Database

3. User Record

4. Generate Token

5. Call Patient Management Service (Zuul Dynamic Routing)

6. Direct Call Patient Service (Token Verify From Auth Server)
Note: Without a token, you can't call.

7. Call Clinic Management Service (Zuul Dynamic Routing)
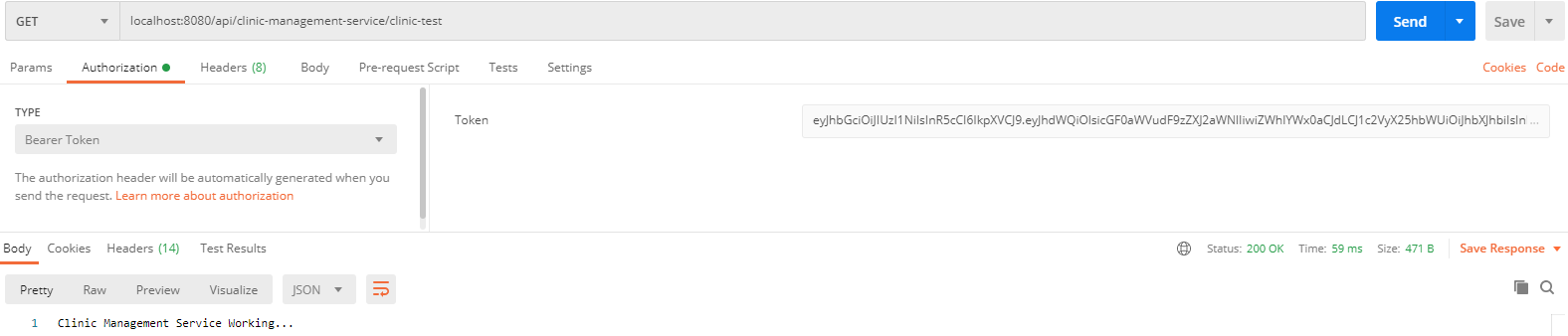
Conclusion
I am trying to show OAuth2 implementation in microservice architecture with secure communication, single entry point, dynamic routing, fail-back solutions, centralized configurations, and OAuth2-client implementation in service to secure every API and every request to ensure authorization.
Source Code
The full source code can be found here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments